Abstract
Introduction
Emerging literature suggests body mass index (BMI) may be increasing in individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD), a condition historically associated with underweight status. However, the current prevalence of overweight and obese adults with SCD remains unclear in a country where high BMI is prevalent in the general population. We present an epidemiological analysis of the prevalence of overweight and obese individuals in a large representative sample of adult SCD patients, identifying associations between BMI, sociodemographic and clinical characteristics.
Methods
Using the Sickle Cell Disease Consortium (SCDIC) registry, we compiled a detailed clinical and demographical from a non-random sample of adults, aged 20-45 years. The SCDIC collects data from eight academic centers providing comprehensive care throughout the U.S. Adult participants were excluded from the analysis if they were under 20 years of age, pregnant at the time of enrollment, or were without medical records or patient enrollment surveys. Sociodemographic information and patient-reported outcomes, including pain frequency and severity, SCD complications, and hydroxyurea use, were collected at the time of enrollment. Non-SCD medical conditions and anthropometric measurements were abstracted from medical records. We stratified BMI, measured in kilograms per meters squared (kg/m2) following CDC criteria: underweight (<18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0-29.9 kg/m2), and obese (>30 kg/m2). An epidemiological analysis was performed of BMI in those with SCD. Bivariate analyses were conducted using Chi-square test, t-test, and ANOVA; non-parametric tests were used when appropriate. Data were analyzed using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute; Cary, NC).
Results
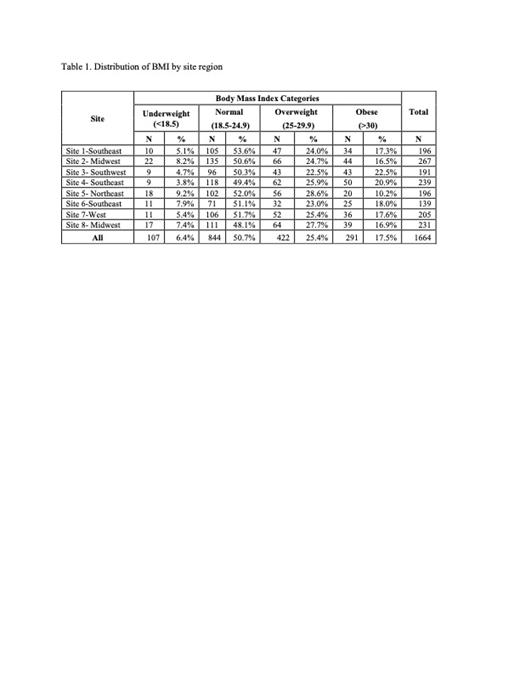
In total, 1,664 adults met the inclusion criteria for this cross-sectional analysis of SCDIC registry data. The median BMI for the entire sample was 23.9 kg/m² (IQR: 21.1-28). The majority of participants were African American (99.1%), female (56.6%), and had an HbSS genotype (69.6%). The prevalence of an obese BMI (17.5%) was greater than underweight BMI (6.4%) among the entire cohort (Table 1). When compared to under/normal weight participants, those who were overweight/obese were older (median age 31.2 versus 29.3 years; p<0.0001) and had a higher prevalence of hypertension (45.1% versus 28.3%; p<0.0001). Most participants in the overweight/obese BMI categories had genotype HbSS (59.0%), however, genotype HbSS accounted for 77% of the under/normal weight category. Most participants with an overweight/obese BMI also had some college or vocational training (39.9%) and had Medicare, Medicaid, or military insurance (71.9%). Median BMI did not differ on reported use or non-use of hydroxyurea (23.9 [IQR: 21.1-27.6] vs 23.9 [IQR: 21.0-28.4] p=0.1), mean number of patient-reported SCD complications (2.6 versus 2.6; p=0.6), nor mean pain frequency (49.6 versus 50.6; p=0.06). However, overweight/obese participants reported significantly higher mean pain intensity than their under/normal weight counterparts (51.8 versus 50.8; p=0.03).
Conclusion
To date, this is the largest analysis of adult BMI among individuals with SCD in the U.S. Among the eight SCDIC sites spanning from the Northeast to Southwest U.S., the prevalence of underweight BMI was less than that of overweight or obese BMI status, challenging previous understandings of weight status and further aligning with the growing rates of overweight and obesity in the general U.S. population. Significant associations between high BMI and hypertension, age, and pain intensity highlight an opportunity for further research to understand the impact of increasing BMI on SCD outcomes and non-SCD comorbidities.
Ibemere: bluebird bio Insights Council: Consultancy, Honoraria; Ugali Youth: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. King: Health Resources and Services Administration: Research Funding; National Cancer Institute: Research Funding; Global Blood Therapeutics: Research Funding; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Research Funding. Hankins: Global Blood Therapeutics: Consultancy; UpToDate: Consultancy; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Vindico Medical Education: Consultancy. Tanabe: CSL Behring: Consultancy. Shah: Emmaus: Consultancy; GLG: Consultancy; Alexion: Speakers Bureau; Guidepoint Global: Consultancy; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; GBT: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal